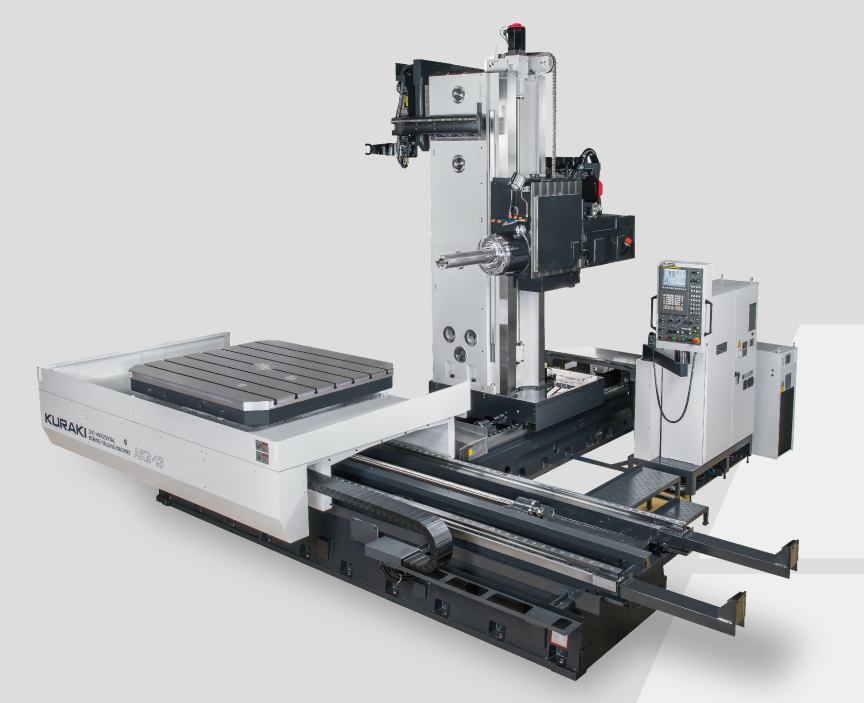
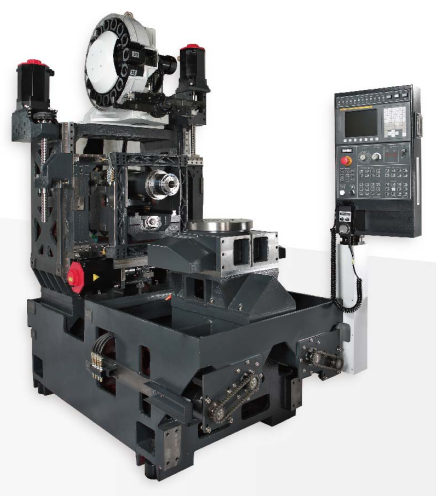
1 Horizontal Machining Center
A horizontal machining center is a machining center where the spindle is placed horizontally.2 Number of feed axes
Horizontal machining centers can be divided into 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis vertical machining centers based on the number of feed axes.
If the turning function is assigned to the table of a 5-axis machining center, it is classified as a 5-axis millturn horizontal machining center.
2.1 3-ax HMC
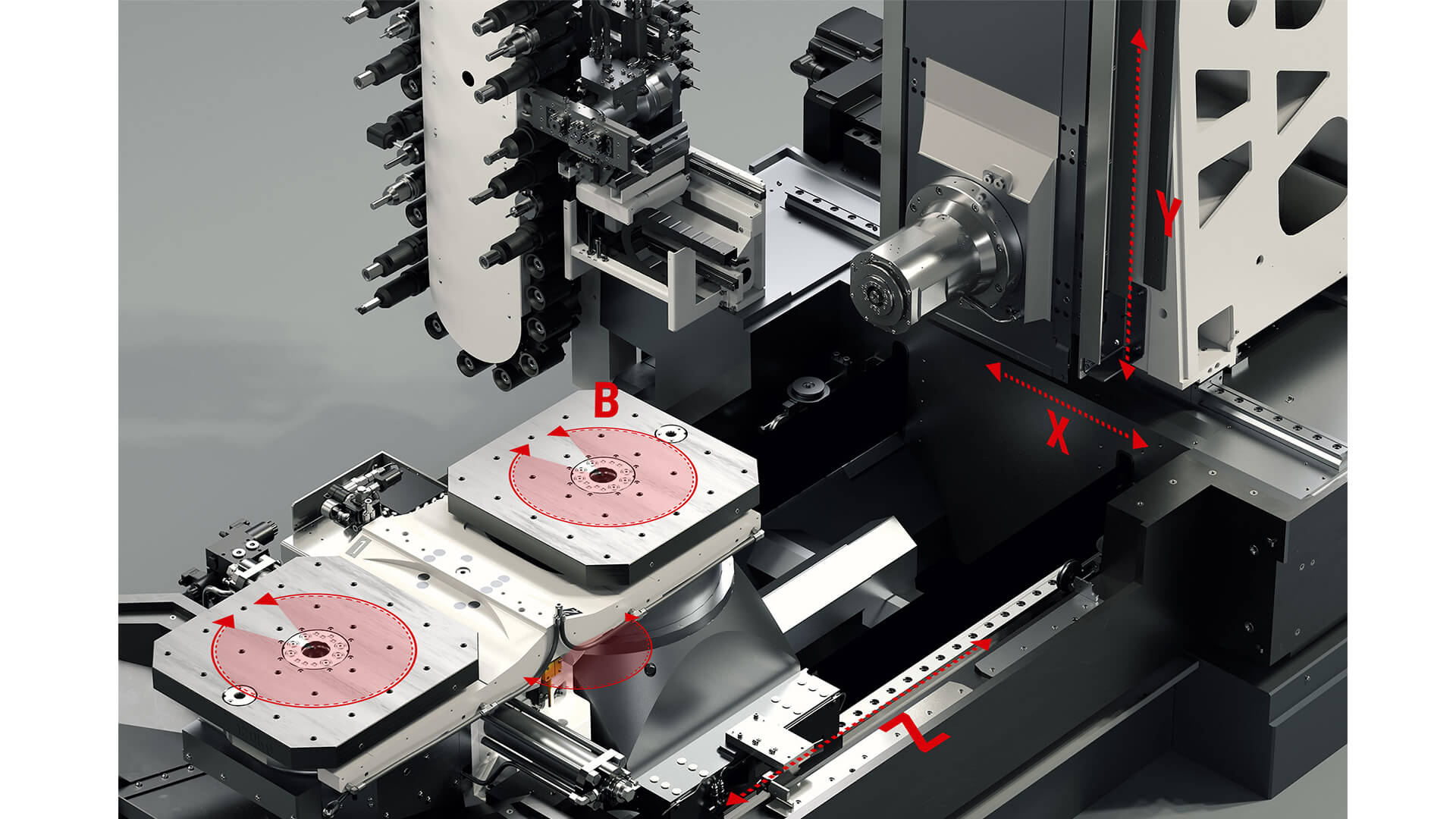
The 3-axis horizontal machining centers are mostly composed of three axes (X, Y, Z).
2.2 4-ax HMC
The 4-axis horizontal machining centers consist of three linear movement axes (X, Y, Z) and one rotational movement axis (one of A, B, C). The characteristics of the machine can vary greatly depending on the position of the rotational axis.
2.3 5-ax HMC
The 5-axis horizontal machining center consists of three linear axes (X, Y, Z) and two rotational axes (two of A, B, C). The characteristics of the machine can vary greatly depending on the position of the rotational axes.
2.4 5-ax millturn HMC
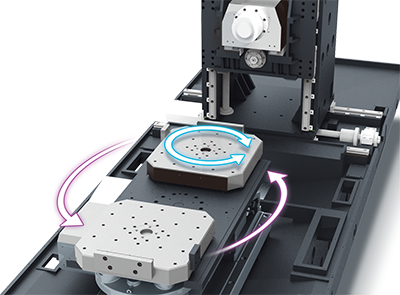
The 5-axis millturn horizontal machining centers consist of three linear axes (X, Y, Z) and two rotational axes (two of A, B, and C). Its table is equipped with a turning function.
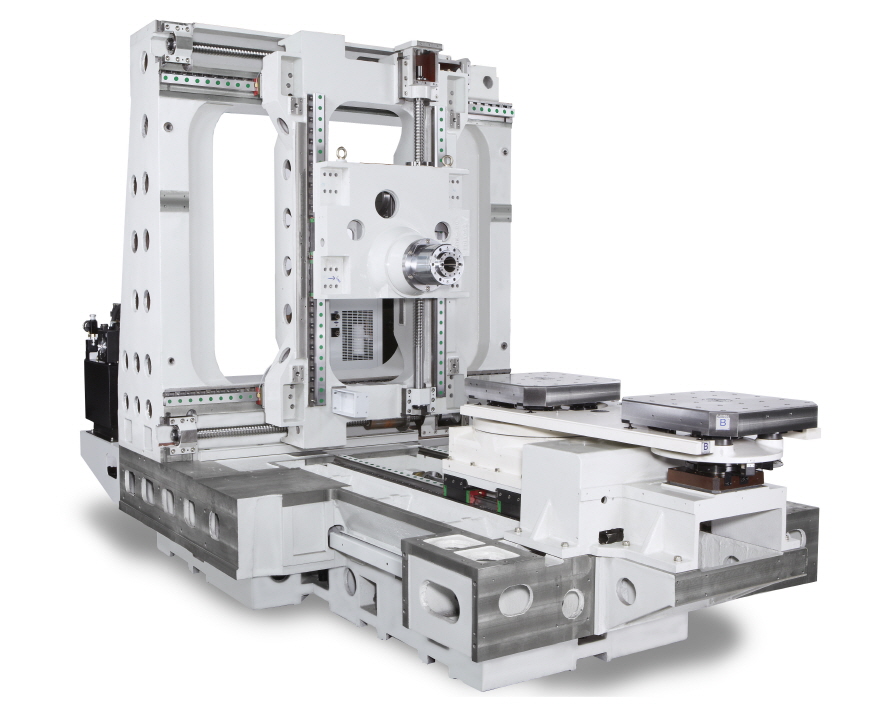
3 Machine structure3-1. Bed type
Bed type refers to the boring machine with a table on the bed, the table forms the X or Z axis. The bed types are further divided into table type, planer type, and reversed-T type.
The bed is equipped with a saddle to form the Z-axis, and the saddle is equipped with a table to form the X-axis. The column is fixed, and the milling spindle head is mounted on the column to form the Y-axis and moves up and down.
The bed is directly equipped with a table to form the X-axis, and the column is mounted on the bed to form the Z-axis. The milling spindle head is mounted on the column to form the Y-axis and moves up and down.
T-shape HMC is similar to planer type horizontal boring machine in structure.
Also known as a T-shaped horizontal machining center.
The bed is directly equipped with a table to form the Z-axis, and the column is mounted on the bed to form the X-axis. The milling spindle head is mounted on the column to form the Y-axis and moves up and down.
3-1-4 Box-in-box type horizontal machining center
A frame is set on top of the bed and a square box-shaped slide placed on this frame to form the X-axis. Two guide rails and drive axes are arranged at both ends. Another square box shaped slide is placed inside the X-axis slide, forming the Y-axis.
3-1-5 Vertial Box-in-box type horizontal machining center
A frame is set on top of the bed and a square box-shaped slide placed on this frame to form the Y-axis. Two guide rails and drive axes are arranged at both ends. Another square box shaped slide is placed inside the Y-axis slide, forming the X-axis.